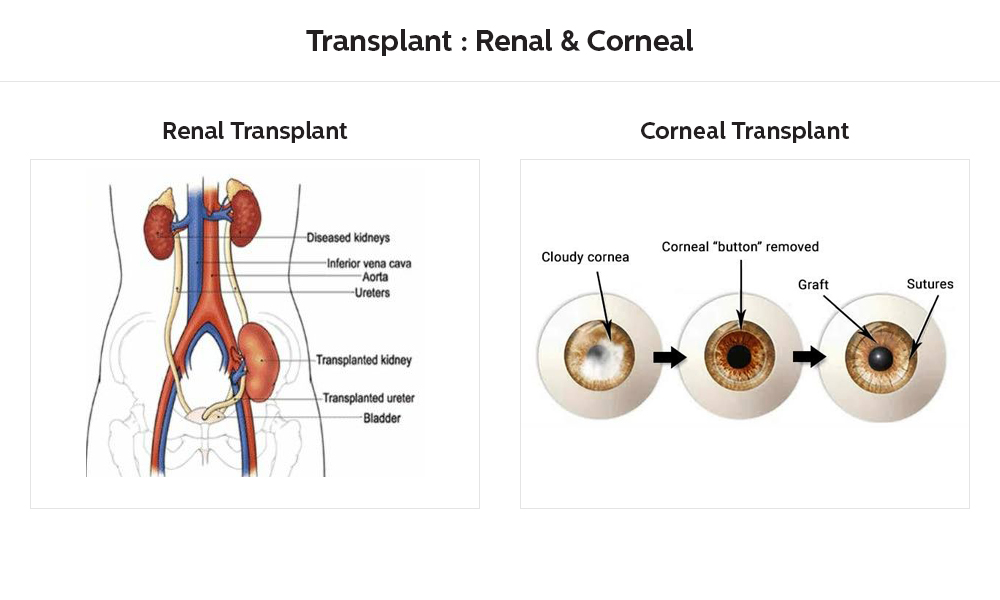
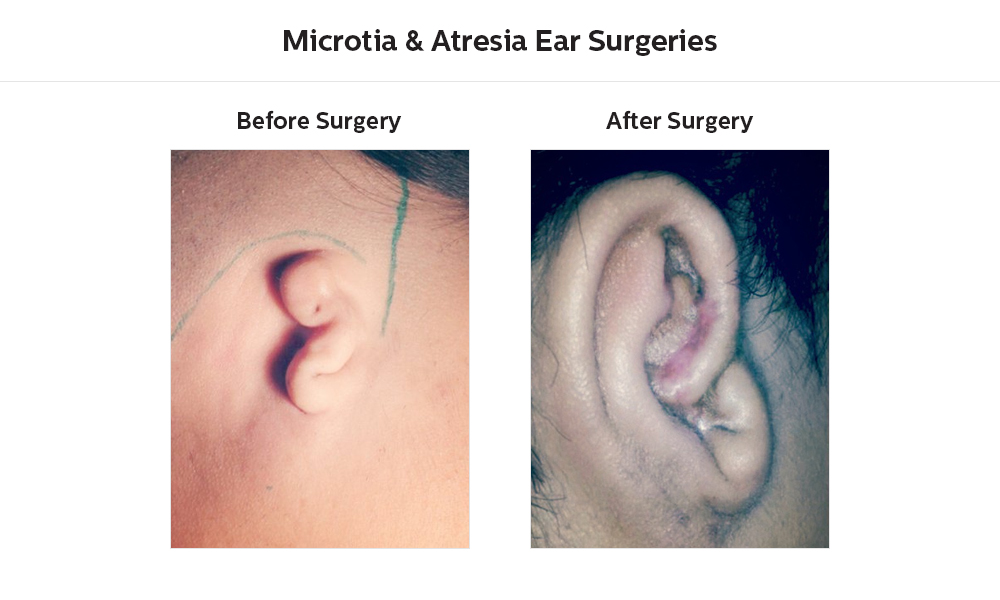
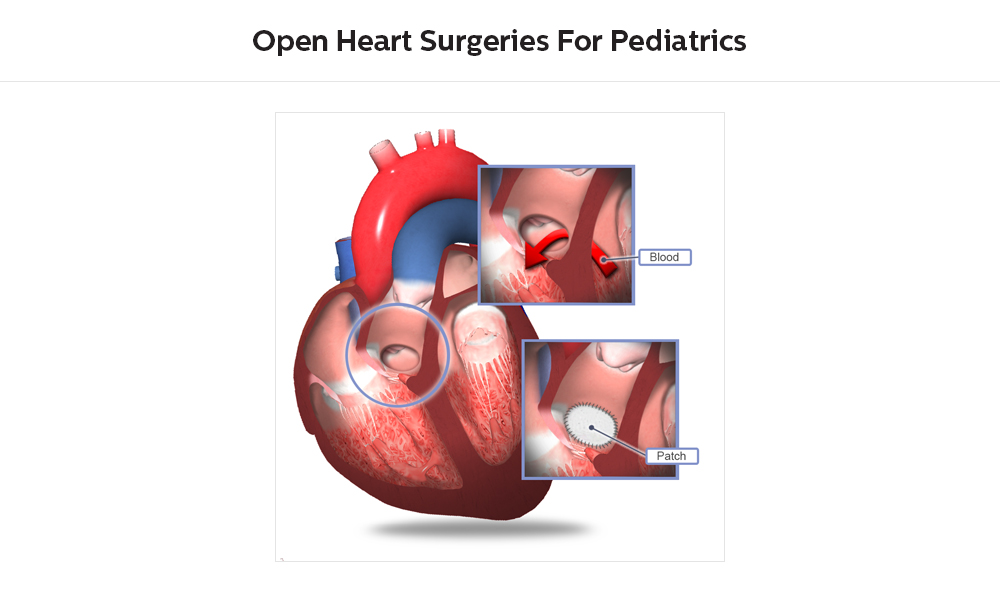
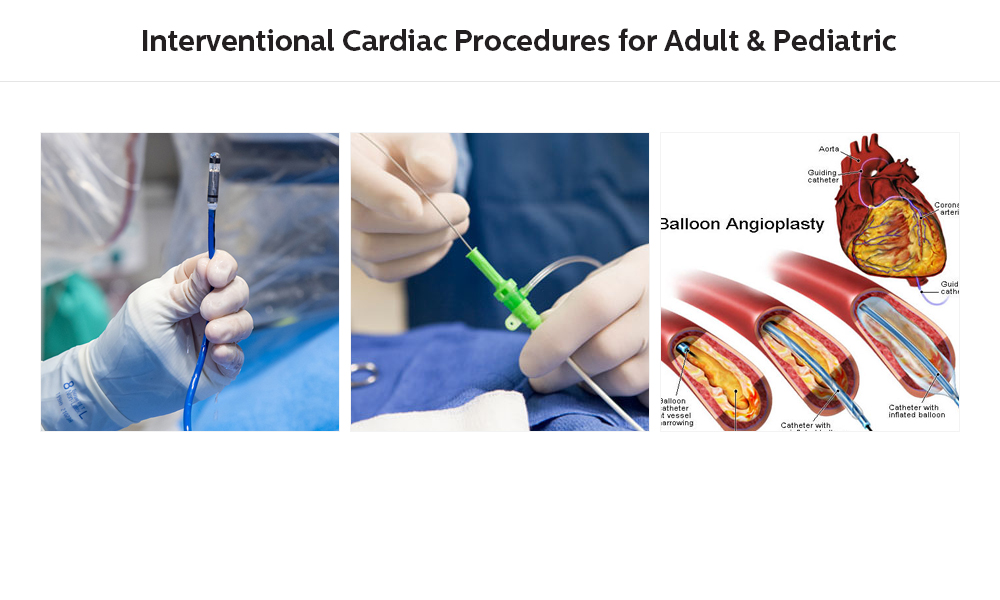
The 28th of July is observed as “World Hepatitis Day”. As per the World Health
Organisation (WHO) Global Hepatitis Report of 2017, this day is chosen as an
opportunity to generate awareness and set up national as well as international efforts to
set up treatments for Hepatitis.
July 28 marks the birth anniversary of the Nobel-prize-winning scientist Dr Baruch
Blumberg. Dr Baruch Blumberg discovered the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and developed a
diagnostic test and vaccine for the virus.
Today, despite a dedicated day to raise awareness about Hepatitis, many don’t know what
this disease is, its symptoms, causes and treatment. Being aware of Hepatitis is the 1st
step to fight it. Therefore, we have prepared a concise guide to help you understand the
disorder better.
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is the inflammation or swelling of the Liver. The primary function of the Liver
is to produce bile that aids in digestion. Apart from this, it also helps in flushing toxins
from the body and retaining vitamins and minerals. A swelling in the Liver usually
develops when the body’s tissues are injured or injected. The inflammation stops the liver
from functioning normally, which can severely impact the whole body.
Types of Hepatitis
There are 5 classified types of Hepatitis. These are:
- Hepatitis A: A short-term, acute disease resulting from an infection from the
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV). One can get infected with this disease if they come in
contact with water or food contaminated with faecal matter of Hepatitis A infected
person. - Hepatitis B: Compared to Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B is a chronic condition. One is
affected with Hepatitis B via the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). Hepatitis B is
transmitted if you come in contact with the bodily fluids such as semen, blood or
vaginal fluids of an infected person. - Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C is the common form of bloodborne disease caused due to
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). This infection is transmitted through exposure to blood
due to unsafe injection practices, sexual practices and unscreened blood
transfusions. - Hepatitis D: Hepatitis D is a rare form of the disease. It occurs when a person
becomes infected with both Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D (co-infection) or gets
infected with Hepatitis B first and then Hepatitis D (super-infection). - Hepatitis E: Found in poor sanitation areas, Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease
transmitted through Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). This disease is typically transmitted
through consumption or injection of contaminated water.
Causes of Hepatitis - Hepatitis A: Exposure to HAV in food and water
- Hepatitis B: Exposure to HBV through bodily fluids
- Hepatitis C: Exposure to HCV through blood
- Hepatitis D: Exposure to Hepatitis B and then Hepatitis D
- Hepatitis E: Exposure to HEV in water
- Other Causes: a. Fatty Liver b. Liver failure or damage due to alcohol
consumption c. Immune cells in the body attacking the Liver d. Overdose of
medicines that can affect the liver.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Even if infected, many are unaware they are suffering from Hepatitis. The following
symptoms can act as a marker to judge Hepatitis. - Fatigue
- Pain or Bloating in the belly area
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Flu-like symptoms
- Itching
- Dark urine
- Pale or grey-coloured stools
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (Yellowing of skin or eyes)
One must seek immediate medical assistance if they are infected with any of the 5
Hepatitis types or are experiencing any of the above symptoms of Hepatitis.
Diagnosis for Hepatitis
It is difficult to assess what is causing hepatitis. Hence, the doctors will conduct a series
of tests:
- History and Physical Examination: Upon consulting your doctor, he will ask
you about your medical history and whether you have travelled, indulged in
unhygienic practices or physically come in contact with someone in the past few
days/weeks. Next, the doctor will physically assess the pain areas and check for
joint pain, swelling or discolouration of the eyes. - Blood Tests: Blood tests are done to detect the problem.
- Liver Function Test: Through a blood test, your doctor can evaluate whether the
liver is functioning well or if there is parasite formation. - Liver Biopsy: While diagnosing hepatitis, the doctors also need to consider the
liver for potential damage. Hence, a liver biopsy is conducted wherein a sample of
the tissues in the liver is taken for examination. - Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound creates images of the organs in the
abdomen. This helps the doctors get a closer look at the liver and the surrounding
organs. An ultrasound helps reveal fluid in the gut, liver damage and liver tumour.
Treatment for Hepatitis
The treatment for each type of Hepatitis varies as follows: - Hepatitis A: As mentioned above, Hepatitis A is an acute and short-term infection.
There is no specific cure for this disease. It goes away with proper rest and medicines. - Hepatitis B: Vaccine for Hepatitis B is available in India for all age groups.
- Hepatitis C: No vaccine for Hepatitis C is available. However, it can be cured through
anti-viral drugs. - Hepatitis D: Hepatitis B vaccine is used to treat Hepatitis D infection.
- Hepatitis E: For Hepatitis E, doctors recommend proper rest and anti-viral medicines.
Join Hands on World Hepatitis Day to End the Silent Epidemic
On 28th July, connect with your nearest doctor to better understand Hepatitis. Pledge to
educate the people around you about this ignored battle and provide the suitable means and
resources to fight and eradicate this disease.